CinemaThe top ten new archaeological discoveries in the country in 2023 are unveiled, and the coverage of time and space is unprecedented.
Text/Yangcheng Evening News All-Media Reporter Literature and Art Photo/Guangdong Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology
3Komiks From March 21st to 22nd, the final review of the top ten archaeological new discoveries of the 2023 National sponsored by China Cultural Relics Newspaper and the Chinese Archaeology Society was held in Beijing. After project report meeting and comprehensive review, the judges finally voted to select the top ten new archaeological discoveries in the country in 2023. Guan Qiang, deputy director of the National Bureau of Culture and Arts and vice chairman of the Chinese Archaeology Society, announced the final results and was selected as one of the top ten Komiks projects (sorted by yearly yearly Babaylan): Yishui Bashan Site Group, Pingtan Jiqiutou Site Group, Pingtan, Fujian, Mopanshan Site Group, Langxi, Anhui, Qujialing, Jingmen, Hubei href=”https://comicmov.com/”>Babaylan site, Wangzhuang site in Yongcheng, Henan, Shangdu Academy Street Cemetery in Zhengzhou, Henan, Zhaigou site in Qingjian, Shaanxi, Sijiaoping site in Li County, Gansu, Chencun porcelain kiln site in Chenzhou, Chenzhou, Shanxi, and Shipwreck site in Lupo, No. 1 and No. 2, northwest of the South China Sea.
Yanshanzhai changed the academic community’s understanding of the origin process of Lingnan civilization
The reporter learned from the final review meeting that Neolithic archaeology will have fruitful results in 2023, so the competition for projects during this period is particularly fierce. Among the 22 final review projects, 8 of the 22 final review projects belong to the Neolithic Age, and 4 were finally selected. Expert representative of the judges, Chen Xingcan, researcher and director of the Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, emphasized that the 22 projects entering the final evaluation have important academic value and great scientific significance, regardless of whether they are finally selected or not.
Chen Xingcan took the “Guangdong Yingdeyan Mountain Village Site” in the Neolithic Age as an example and believed that the Yanshan Village Site changed the understanding of the origin of civilization and social complications in the Lingnan region. “We had insufficient understanding of Lingnan in the past. Now, it entered a complex social stage 4,800 years ago. The origin of civilization is actually synchronized with the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, which has greatly changed our understanding of the degree of social development in this region.”He said.
In answering reporters’ questions, he also introduced that the 22 projects shortlisted for the final review this year cover a wide range of time and space, from the “Tibet Gejimeilongdapu Cave Site” in the Paleolithic Age 100,000 years ago to the “Hongshi Mazi Site in Panshi City, Jilin Province” eight or ninety years ago. In terms of time, the 22 projects range from the southeast coast to the northwest border, from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of 4,700 meters to the underwater sinking ship of 1,500 meters underwater on the northwest slope of the South China Sea, with a space range of a wide range of href=”https://comicmov.com/”>Cinema is large. The 22 final review projects also reflect multidisciplinary cooperation, meticulous excavation, and cultural relics. href=”https://comicmov.com/”>BabaylanThe unprecedented improvement in protection awareness is outstanding.
The earliest complex society that can be confirmed in Lingnan area
Yanshanzhai site is located in Lan Village, Qingtang Town, Yingde City, Qingyuan City, Guangdong Province. It is located in the middle of the mountain area in northern Guangdong and the Pearl River Delta, with an area of about 100,000 square meters.
From 2019 to 2023, the Guangdong Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, in conjunction with Sun Yat-sen University, Peking University and other units, continued to carry out active archaeological excavations of the site, with an excavation area of 2,900 square meters, and cleared out tombs, ash pits, ash ditches, column holes (groups), stoves and burnt mounds from the Neolithic era toCinema Important relics of the Xia and Shang dynasties, and more than 4,300 samples of various cultural relics such as jade, pottery, grinding stone, bronze, human bones and plant remains were unearthed.
According to the project leader and director of the Pre-Qin Archaeology Institute of Guangdong Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, the archaeological excavation of the Yanshanzhai site has achieved many aspects of gain. The most important harvest is the discovery of large cemeteries of the late Neolithic Age at the Yanback site. The exploration confirmed area is about 5,000 square meters, the exposed area is 1,200 square meters, and 93 tombs are cleared. More than 1,200 burial objects such as jade, pottery, stone tools, etc. are unearthed from Komiks. The cemetery can be seen with clear zoning and grouping plans, and it is the largest and clearest structural layout of Shixia cultural cemetery that has seen so far./p>
The rock-back cemetery does not have significant gaps in the rich and poor and grade differences between tombs in the same district and group. Among them, the highest-level M16 burial objects have as many as 145, including 5 jade axes and 74 stone horns, and M26 is buried with jade cong and jade axes at the same time. The Yanbei Cemetery clearly reflects the accelerated social differentiation around 4,800 years ago and forms institutionalized burial customs. This is the earliest complex society that can be confirmed in the Lingnan region during the origin of Chinese civilization.
At the same time, the dating data of the Rock Behind Tombs are concentrated between 5,000 and 4,000 years ago, which updates the previous understanding of the upper and lower limits of the Shixia cultural era. Through the multi-level dissection of typical tombs, the burial process was completely restored, and a clearer understanding of the burial customs of Shixia culture was found.
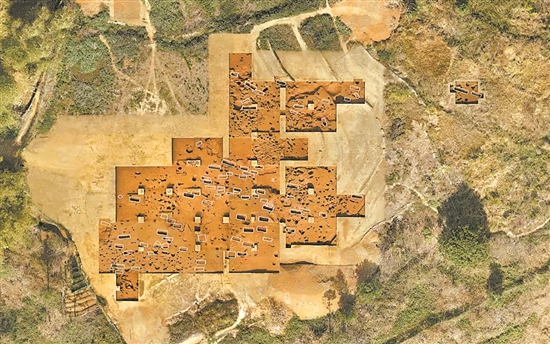
The most important archaeological discovery of Lingnan Neolithic Age
The Yanshanzhai site, which is being continuously excavated by the industry, has been widely recognized by the State Administration of Cultural Heritage in 2021 as a major project achievement of “Archaeological China”.

Liu Suoqiang pointed out that the archaeological achievements of the Yanshanzhai site confirm that Lingnan has entered a complex social stage about 4,800 years ago, and show the role of diversified integration in the civilized process of Lingnan region, and also reflect that Lingnan has a regional social complex model different from the Yangtze River Basin.
Not only that, abundant rice remains were found in the tombs, buildings and ash pit ruins of the Yanshanzhai site, indicating that the middle reaches of the Beijiang River where it is located is a crucial intermediate node on the rice farm agricultural transmission route from Lingbei to northern Guangdong and then to the Pearl River Delta, and it is also an important node for Lingnan to integrate into the process of China’s civilization integration. The discovery helps to reinterpret the Shixia culture and the status of the Lingnan region in archaeological cultural areas.
The reporter learned that since the selection of the top ten archaeological new discoveries in the country in 2023, the participation trends of the Yanshanzhai site have been closely watched by the Guangdong archaeological industry. At present, the Yanshanzhai site is still being excavated, and with its archaeology and research work, it hasContinued development will continue and will remain a strong competitor to this important national archaeological award in the future.
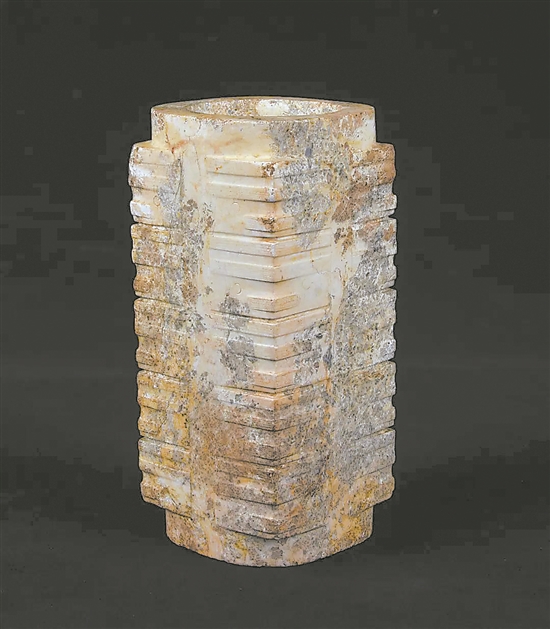


ArchaeologyKomiksThe excellent base for professional students to move into the fields
Yanshanzhai Site is a cooperative project between the Guangdong Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology and the School of Sociology and Anthropology of Sun Yat-sen University to build the “Guangdong Field Archaeology Research Base”. Since 2020, students from Sun Yat-sen University’s archaeology majoring in Cinema have successively gone to the Yanshanzhai site to complete their field archaeology internship.
The reporter learned that field archaeology internship is a professional compulsory course for undergraduates of Sun Yat-sen University’s Department of Archaeology. It is usually conducted in the first semester of junior high school and lasts for one semester. The Yanshanzhai site covers ancient tombs and living functional areas. Teachers and students from Zhongda mainly carry out practical training in field archaeological excavations in the living functional areas.
Zhou Fanwen said that there is currently a large gap in front-line archaeological talents, so archaeology students are required to master the basic operating procedures for field archaeological excavation before graduation. During the six-month internship, students entered the construction site for field archaeological excavation in the first three months, followed by the unearthed artifacts, and finally formed internship results that were preliminary judgments on the age, nature, and cultural appearance of the excavated area.
In addition, teachers will also encourage students who want to continue their studies and guide them to use first-hand archaeological data to carry out follow-up Komiks research. Zhou Fanwen believes that such training is very helpful for students to carry out higher-level research in the future and is their first ladder toward the academic hall.
Zhou Fanwen also said: “Our students are very lucky to be able to contact the archaeological excavation of the Yanshanzhai site at the introductory stage. This is an archaeological site selected as the major project of ‘Archaeological China’. On-site participation undoubtedly provides them with the most complete and systematic training.”
Continue to promote the construction of Qingtang Archaeological Site Park
The archaeological excavation team of the Yanshanzhai site, and its members also have workers from local cultural and museum institutions.Staff. Liu Jianwen, director of Yingde Museum, is one of them and has participated in a lot of practical work. Liu Jianwen said that local museums are more about assisting work, such as providing restoration sites for unearthed cultural relics, and coordinating the relationship between the archaeological team and local villagers. He emphasized: “The hardest test is done by professionals, and what we can do is provide them with the most convenient logistical support.” However, as a native of Yingde, Liu Jianwen is deeply proud of his hometown having such a major archaeological discovery. He told reporters: “I am very honored to be able to participate in such an important archaeological excavation project. This is a rare opportunity in our career for grassroots cultural and museum workers. At the same time, we also feel a great responsibility and will assist in the continuous excavation of the site, as well as protection, interpretation, display and other work.” Liu Jianwen also Babaylan said that the local area is actively promoting the construction of Qingtang Archaeological Site Park. It is reported that the standard scope of Qingtang Archaeological Site Park is centered on the distribution of the remains of Qingtang ruins and Yanshanzhai ruins. It was approved by the State Administration of Cultural Heritage in 2022 and was included in the fourth batch of national archaeological ruins park project list.
“From Guangdong Province to Qingyuan City and then to Yingde City, leaders at all levels attach great importance to the progress of Qingtang Archaeological Site Park. The construction of the park requires a lot of investment and involves coordination and linkage between multiple parties, so it cannot be achieved overnight. I believe that the public and the media attach great importance to the Cinema Yanshanzhai Site and the ‘Early Lingnan Source Exploration Project’ will create a better research and construction atmosphere.” Liu Jianwen said.